INTERSTELLAR 88/8: EXTREME WEIGHTLOSS PROTOCOL
April 17, 2019
AMPK
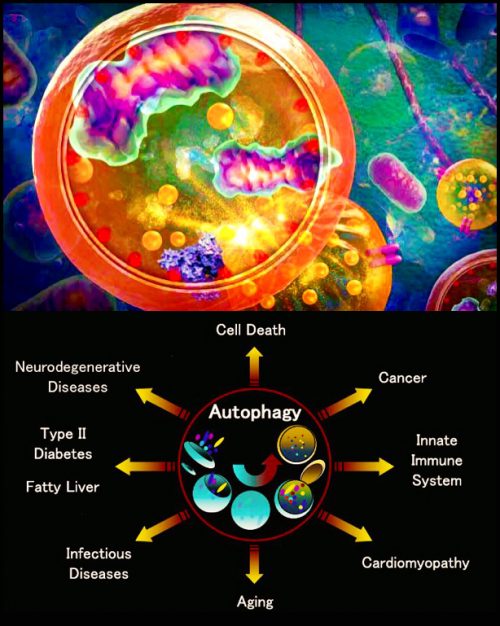
May 1, 2019Autophagy (or autophagocytosis) (from the Ancient Greek αὐτόφαγος autóphagos, meaning “self-devouring”[1] and κύτος kýtos, meaning “hollow”[2]) is the natural, regulated mechanism of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components.[3] It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components.[4][5]
Three forms of autophagy are commonly described: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). In macroautophagy, expendable cytoplasmic constituents are targeted and isolated from the rest of the cell within a double-membraned vesicle known as an autophagosome,[6][7] which, in time, fuses with an available lysosome, bringing its specialty process of waste management and disposal; and eventually the contents of the vesicle (now called an autolysosome) are degraded and recycled.
In disease, autophagy has been seen as an adaptive response to stress, promoting survival of the cell; but in other cases it appears to promote cell death and morbidity. In the extreme case of starvation, the breakdown of cellular components promotes cellular survival by maintaining cellular energy levels.
The name “autophagy” was in existence and frequently used from the middle of the 19th century[8]. In its present usage, the term autophagy was coined by Belgian biochemist Christian de Duve in 1963 based on his discovery of the functions of lysosome.[3] The identification of autophagy-related genes in yeast in the 1990s allowed researchers to deduce the mechanisms of autophagy,[9][10][11][12][13] which eventually led to the award of the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Japanese researcher Yoshinori Ohsumi.[14]
1000 Scientific Studies all about Autophagy:
- Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease
- Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion
- Autophagy: process and function
- Methods in Mammalian Autophagy Research
- Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism
- Autophagy and Metabolism
- Autophagy: Renovation of Cells and Tissues
- Autophagy as a Regulated Pathway of Cellular Degradation
- Autophagy in immunity and inflammation
- Autophagy and Aging
- Autophagy and the Integrated Stress Response
- mTOR regulation of Autophagy
- Regulation Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways of Autophagy
- Role of Autophagy in cancer
- Bcl-2 Antiapoptotic Proteins Inhibit Beclin 1-Dependent Autophagy
- Induction of Autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1
- Autophagy in Health and Disease: A Double-Edged Sword
- Methods for monitoring Autophagy
- AMPK and mTOR regulate Autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1
- LC3 and Autophagy
- The role of Autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period
- Death by design: apoptosis, necrosis and Autophagy
- Autophagy in cell death: an innocent convict?
- TFEB Links Autophagy to Lysosomal Biogenesis
- Development by Self-Digestion: Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Functions of Autophagy
- Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms
- A protein conjugation system essential for Autophagy
- Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between Autophagy and apoptosis
- Autophagy: molecular machinery for self-eating
- Suppression of basal Autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice
- Autophagy in Human Health and Disease
- Loss of Autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice
- Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their Autophagy
- Potential therapeutic applications of Autophagy
- Apoptosis, Autophagy, and more
- Autophagy Suppresses Tumorigenesis through Elimination of p62
- Mammalian Autophagy: core molecular machinery and signaling regulation
- LC3 conjugation system in mammalian Autophagy
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Triggers Autophagy
- Autophagy and cancer
- The Beclin 1 network regulates Autophagy and apoptosis
- Escape of Intracellular Shigella from Autophagy
- Impaired Degradation of Mutant α-Synuclein by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy
- Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity
- Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive Autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice
- A Role for Ubiquitin in Selective Autophagy
- Autophagy: dual roles in life and death?
- Isofation and charact~~zation of Autophagy-defective mutants of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Autophagy Defends Cells Against Invading Group A Streptococcus
- Autophagy as a cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism
- Regulation of Mammalian Autophagy in Physiology and Pathophysiology
- Autophagy: from phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade
- FoxO3 Controls Autophagy in Skeletal Muscle In Vivo
- A Unified Nomenclature forAutophagy-related genes
- Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation
- Lysosomes and Autophagy in cell death control
- Regulation of Autophagy by cytoplasmic p53
- Autophagy: in sickness and in health
- Network organization of the human Autophagy system
- Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and elimination by Autophagy
- Autophagy: assays and artifacts
- Autophagy Is Activated for Cell Survival after Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- Autophagy, Immunity, and Microbial Adaptations
- A key role for Autophagy and the Autophagy gene Atg16l1 in mouse and human intestinal Paneth cells
- Endogenous HMGB1 regulates Autophagy
- Human IRGM Induces Autophagy to Eliminate Intracellular Mycobacteria
- Tor, a Phosphatidylinositol Kinase Homologue, Controls Autophagy in Yeast
- Autophagy mediates the mitotic senescence transition
- The molecular machinery of Autophagy: unanswered questions
- Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis
- The role of Autophagy in neurodegenerative disease
- Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases
- Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 Autophagy gene
- Dynamics and diversity in Autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast
- Autophagy-Dependent Viral Recognition by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells
- Toll‐like receptors control Autophagy
- The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, Autophagy and metabolism
- Autophagy
- The role of Autophagy in cancer development and response to therapy
- p62/SQSTM1 Binds Directly to Atg8/LC3 to Facilitate Degradation of Ubiquitinated Protein Aggregates by Autophagy
- Pancreatic cancers require Autophagy for tumor growth
- Autophagy in the Eukaryotic Cell
- Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches Autophagy to apoptosis
- α-Synuclein Is Degraded by Both Autophagy and the Proteasome
- Autophagy Is Required to Maintain Muscle Mass
- Self-consumption: the interplay of Autophagy and apoptosis
- Autophagy-deficient mice develop multiple liver tumors
- Induction of Autophagy by spermidine promotes longevity
- Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and Autophagy
- ULK-Atg13-FIP200 Complexes Mediate mTOR Signaling to the Autophagy Machinery
- Lithium induces Autophagy by inhibiting inositol monophosphatase
- The Role of Autophagy in Cancer: Therapeutic Implications
- Emerging regulation and functions of Autophagy
- Loss of the Autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1β production
- Autophagy Is a Defense Mechanism Inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Survival in Infected Macrophages
- Autophagy regulation by p53
- ROS, mitochondria and the regulation of Autophagy
- Autophagy, amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer disease
- Molecular dissection of Autophagy: two ubiquitin-like systems
- Deconvoluting the context-dependent role for Autophagy in cancer
- The Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy
- Phosphorylation of the Autophagy Receptor Optineurin Restricts Salmonella Growth
- Oxidative Stress and Autophagy
- Beclin 1, an Autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor
- Autophagy and human diseases
- Homeostatic Levels of p62 Control Cytoplasmic Inclusion Body Formation in Autophagy-Deficient Mice
- Autophagy in chronically ischemic myocardium
- Autophagy and Cell Death
- DRAM, a p53-Induced Modulator of Autophagy, Is Critical for Apoptosis
- Tor-Mediated Induction of Autophagy via an Apg1 Protein Kinase Complex
- JNK1-Mediated Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 Regulates Starvation-Induced Autophagy
- p62 at the Crossroads of Autophagy, Apoptosis, and Cancer
- Autophagy suppresses tumor progression by limiting chromosomal instability
- Growth Factor Regulation of Autophagy and Cell Survival in the Absence of Apoptosis
- Apoptosis and Autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease
- The Double-Edged Sword of Autophagy Modulation in Cancer
- Autophagy genes in immunity
- Reactive oxygen species are essential for Autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4
- Regulation of Autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology
- The regulation of Autophagy – unanswered questions
- Can Autophagy promote longevity?
- Mitochondrial Autophagy Is an HIF-1-dependent Adaptive Metabolic Response to Hypoxia
- Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 Association with the ULK1–Atg13–FIP200 Complex Required for Autophagy
- Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: cross-talk and redox signalling
- Nix is a selective Autophagy receptor for mitochondrial clearance
- Protein Turnover Via Autophagy: Implications for Metabolism
- Regulation and role of Autophagy in mammalian cells
- p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by Autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death
- Distinct Roles of Autophagy in the Heart During Ischemia and Reperfusion
- Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases
- Defective Autophagy leads to cancer
- Ambra1 regulates Autophagy and development of the nervous system
- Metabolic Control of Autophagy
- Autophagy: a regulated bulk degradation process inside cells
- Toll-like receptor signalling in macrophages links the Autophagy pathway to phagocytosis
- The role for Autophagy in cancer
- Autophagy and signaling: their role in cell survival and cell death
- Activated Ras requires Autophagy to maintain oxidative metabolism and tumorigenesis
- Eating Oneself and Uninvited Guests: Autophagy-Related Pathways in Cellular Defense
- Ubiquitination and selective Autophagy
- Autophagy in the Cellular Energetic Balance
- The mitochondrial permeability transition initiates Autophagy in rat hepatocytes
- Selective Autophagy: ubiquitin-mediated recognition and beyond
- Unveiling the roles of Autophagy in innate and adaptive immunity
- Autophagy Genes Are Essential for Dauer Development and Life-Span Extension in C. elegans
- The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in Autophagy regulation
- Role of Autophagy in temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells
- HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between Autophagy and the UPS
- In Vivo Analysis of Autophagy in Response to Nutrient Starvation Using Transgenic Mice Expressing a Fluorescent Autophagosome Marker
- Autophagy: Many paths to the same end
- Mechanisms of chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- Autophagy in Cancer: Good, Bad, or Both?
- Autophagy-Mediated Tumor Promotion
- Autophagy and cytokines
- Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy
- Autophagy in metazoans: cell survival in the land of plenty
- Cargo recognition and trafficking in selective Autophagy
- Extensive Involvement of Autophagy in Alzheimer Disease: An Immuno-Electron Microscopy Study
- Endogenous MHC Class II Processing of a Viral Nuclear Antigen After Autophagy
- Autophagy in neurons: a review.
- Aggregate-prone proteins with polyglutamine and polyalanine expansions are degraded by Autophagy
- Age-related Decline in Chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- Autophagy Counterbalances Endoplasmic Reticulum Expansion during the Unfolded Protein Response
- The mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death: a common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and Autophagy
- Autophagy and Human Disease
- Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma
- Autophagy in liver diseases
- Autophagy and related mechanisms of lysosome-mediated protein degradation
- Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates Autophagy in disease pathogenesis
- Inhibition of mTOR induces Autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
- Historical landmarks of Autophagy research
- An Overview of the Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy
- Autophagy in skeletal muscle
- Life and death partners: apoptosis, Autophagy and the cross-talk between them
- During Autophagy mitochondria elongate, are spared from degradation and sustain cell viability
- Principles and Current Strategies for Targeting Autophagy for Cancer Treatment
- Autophagy-Dependent Anticancer Immune Responses Induced by Chemotherapeutic Agents in Mice
- Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression
- Autophagy in yeast demonstrated with proteinase-deficient mutants and conditions for its induction.
- The dynamic nature of Autophagy in cancer
- Autophagy regulates adipose mass and differentiation in mice
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity through Autophagy
- The ubiquitin kinase PINK1 recruits Autophagy receptors to induce mitophagy
- Interactions between Autophagy Receptors and Ubiquitin-like Proteins Form the Molecular Basis for Selective Autophagy
- Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling
- Autophagy mitigates metabolic stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis
- Autophagy basics
- Exercise-induced BCL2-regulated Autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis
- A role for the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of Autophagy
- Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on Autophagy genes
- Role and Regulation of Starvation-Induced Autophagy in the Drosophila Fat Body
- Hypoxia-induced Autophagy: cell death or cell survival?
- Autophagy and other vacuolar protein degradation mechanisms
- NOD2 stimulation induces Autophagy in dendritic cells influencing bacterial handling and antigen presentation
- Autophagy Regulates Programmed Cell Death during the Plant Innate Immune Response
- Autophagy: Basic Principles and Relevance to Disease
- mTOR: a pharmacologic target for Autophagy regulation
- Autophagy and tumorigenesis
- Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome
- The role of Autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and in response to hemodynamic stress
- Activation of antibacterial Autophagy by NADPH oxidases
- Mitochondria and the Autophagy–Inflammation–Cell Death Axis in Organismal Aging
- Autophagy
- Autophagy Inhibition Compromises Degradation of Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway Substrates
- Cellular Autophagy: surrender, avoidance and subversion by microorganisms
- Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders
- Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
- Compromised Autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases
- Autophagy Gene-Dependent Clearance of Apoptotic Cells during Embryonic Development
- Studies on the mechanisms of Autophagy: formation of the autophagic vacuole.
- Autophagy in Ischemic Heart Disease
- Dopamine-modified α-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- Cardiac Autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic stress
- Autophagy, organelles and ageing
- A Novel Response of Cancer Cells to Radiation Involves Autophagy and Formation of Acidic Vesicles
- The selective Autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1
- Autophagy and aging: keeping that old broom working
- Toll-like Receptor 4 Is a Sensor for Autophagy Associated with Innate Immunity
- Autophagy and cancer
- Autophagy Is Essential for Preimplantation Development of Mouse Embryos
- Superoxide is the major reactive oxygen species regulating Autophagy
- Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from Autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure
- Vitamin D3 Induces Autophagy in Human Monocytes/Macrophages via Cathelicidin
- Bif-1 interacts with Beclin 1 through UVRAG and regulates Autophagy and tumorigenesis
- ULK1 induces Autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase
- Autophagy Links Inflammasomes to Atherosclerotic Progression
- Sequence variants in the Autophagy gene IRGM and multiple other replicating loci contribute to Crohn’s disease susceptibility
- Mitochondria-Anchored Receptor Atg32 Mediates Degradation of Mitochondria via Selective Autophagy
- Structural Basis for Sorting Mechanism of p62 in Selective Autophagy
- The apoptosis/Autophagy paradox: autophagic vacuolization before apoptotic death
- Autophagy maintains stemness by preventing senescence
- Blocked Autophagy Sensitizes Resistant Carcinoma Cells to Radiation Therapy
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy: roles in disease and aging
- Autophagy inhibition in combination cancer treatment.
- Novel targets for Huntington’s disease in an mTOR-independent Autophagy pathway
- Senescence, Apoptosis or Autophagy?
- Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: a review of apoptosis, Autophagy and programmed necrosis
- Enhancing Immunity Through Autophagy
- Two Beclin 1-binding proteins, Atg14L and Rubicon, reciprocally regulate Autophagy at different stages
- Activation of Chaperone-mediated Autophagy during Oxidative Stress
- Connecting endoplasmic reticulum stress to Autophagy by unfolded protein response and calcium
- Response to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury involves Bnip3 and Autophagy
- Identification of a candidate therapeutic Autophagy-inducing peptide
- Autophagy in infection
- A block of Autophagy in lysosomal storage disorders
- HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin‐selective quality‐control Autophagy
- Autophagy: for better or for worse
- Regulation of starvation- and virus-induced Autophagy by the eIF2α kinase signaling pathway
- Autophagy promotes MHC class II presentation of peptides from intracellular source proteins
- ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK‐induced cell death – apoptosis, Autophagy and senescence
- Targeting Autophagy in cancer
- Secretory Autophagy
- Cytoprotective roles for Autophagy
- Nod1 and Nod2 direct Autophagy by recruiting ATG16L1 to the plasma membrane at the site of bacterial entry
- Small molecules enhance Autophagy and reduce toxicity in Huntington’s disease models
- Autophagy at the crossroads of catabolism and anabolism
- The Phosphatidylinositol 3‐Kinase Inhibitors Wortmannin and LY294002 Inhibit Autophagy in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes
- The Atg16L Complex Specifies the Site of LC3 Lipidation for Membrane Biogenesis in Autophagy
- Autophagy Induction and Autophagosome Clearance in Neurons: Relationship to Autophagic Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Autophagy and oxidative stress associated with gold nanoparticles
- The Atg12-Atg5 Conjugate Has a Novel E3-like Activity for Protein Lipidation in Autophagy
- The Association of AMPK with ULK1 Regulates Autophagy
- Autophagy: a barrier or an adaptive response to cancer
- Phosphorylation of Ribosomal Protein S6 Is Inhibitory for Autophagy in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes
- The role of Autophagy in the heart
- Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment
- An Overview of Autophagy: Morphology, Mechanism, and Regulation
- The Beclin 1–VPS34 complex – at the crossroads of Autophagy and beyond
- Consequences of the selective blockage of chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- The Microbiome and Butyrate Regulate Energy Metabolism and Autophagy in the Mammalian Colon
- Akt-Mediated Regulation of Autophagy and Tumorigenesis Through Beclin 1 Phosphorylation
- Role and regulation of Autophagy in cancer
- Control of Autophagy by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
- HSV-1 ICP34.5 Confers Neurovirulence by Targeting the Beclin 1 Autophagy Protein
- Dengue Virus-Induced Autophagy Regulates Lipid Metabolism
- Anti- and pro-tumor functions of Autophagy
- Chaperone‐Mediated Autophagy in Aging and Disease
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy: a unique way to enter the lysosome world
- The pleiotropic role of Autophagy: from protein metabolism to bactericide
- Autophagy delays apoptotic death in breast cancer cells following DNA damage
- Autophagy in neurodegenerative disease: friend, foe or turncoat?
- Huntingtin Expression Stimulates Endosomal–Lysosomal Activity, Endosome Tubulation, and Autophagy
- Two Distinct Vps34 Phosphatidylinositol 3–Kinase Complexes Function in Autophagy and Carboxypeptidase Y Sorting inSaccharomyces cerevisiae
- Autophagosome Formation and Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy
- p53: The Janus of Autophagy?
- The LIR motif – crucial for selective Autophagy
- E2F1 regulates Autophagy and the transcription of Autophagy genes
- Cargo recognition failure is responsible for inefficient Autophagy in Huntington’s disease
- Viruses and Autophagy
- Non-selective Autophagy.
- Autophagy in the liver
- Autophagy and neurodegeneration: when the cleaning crew goes on strike
- Autophagy‐based unconventional secretory pathway for extracellular delivery of IL‐1β
- NF-κB Activation Represses Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-induced Autophagy
- Oxidative stress and Autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs
- Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- Physiological Functions of Autophagy
- Autophagy and lysosomal dysfunction as emerging mechanisms of nanomaterial toxicity
- Studies on the mechanisms of Autophagy: maturation of the autophagic vacuole.
- Selective Mitochondrial Autophagy, or Mitophagy, as a Targeted Defense Against Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Aging
- Autophagy facilitates glycolysis during Ras-mediated oncogenic transformation
- Macrophage Autophagy Plays a Protective Role in Advanced Atherosclerosis
- Autophagy: Principles and significance in health and disease
- Autophagy failure in Alzheimer’s disease—locating the primary defect
- Lipophagy: Connecting Autophagy and Lipid Metabolism
- Induction of Autophagy during Extracellular Matrix Detachment Promotes Cell Survival
- The Roles of Therapy-Induced Autophagy and Necrosis in Cancer Treatment
- Autophagy and apoptosis: what is the connection?
- Autophagy as a therapeutic target in cancer
- Autophagy Controls IL-1β Secretion by Targeting Pro-IL-1β for Degradation
- FoxO Transcription Factors Promote Autophagy in Cardiomyocytes
- Autophagy: A lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease
- Trehalose, a Novel mTOR-independent Autophagy Enhancer, Accelerates the Clearance of Mutant Huntingtin and α-Synuclein
- Cerebral Ischemia-Hypoxia Induces Intravascular Coagulation and Autophagy
- Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Markers in Parkinson Disease Brains
- Autophagy and the Immune System
- FLIP-mediated Autophagy regulation in cell death control
- Autophagy and multivesicular bodies: two closely related partners
- The TBK1 adaptor and Autophagy receptor NDP52 restricts the proliferation of ubiquitin-coated bacteria
- Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy Is Mediated through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via Their BH3 Domains
- Activation of Autophagy by inflammatory signals limits IL-1β production by targeting ubiquitinated inflammasomes for destruction
- Lysosomal Proteolysis and Autophagy Require Presenilin 1 and Are Disrupted by Alzheimer-Related PS1 Mutations
- Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for Autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion
- Chaperone-Assisted Selective Autophagy Is Essential for Muscle Maintenance
- Differential Effects of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-induced Autophagy on Cell Survival
- Autophagy in innate and adaptive immunity
- Physiological functions of Atg6/Beclin 1: a unique Autophagy-related protein
- Autophagy in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- ER stress (PERK/eIF2α phosphorylation) mediates the polyglutamine-induced LC3 conversion, an essential step for Autophagy formation
- Autophagy as an immune defense mechanism
- Inflammaging: disturbed interplay between Autophagy and inflammasomes
- Apoptosis, Autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis
- Neutrophil extracellular trap cell death requires both Autophagy and superoxide generation
- Growth Arrest and Autophagy Are Required for Salivary Gland Cell Degradation in Drosophila
- Physiological significance of selective degradation of p62 by Autophagy
- Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the Regulation of Autophagy: Cross Talk, Shortcuts, and Feedbacks
- Autophagy and Cellular Immune Responses
- Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, Autophagy, and mitophagy
- The Adaptor Protein p62/SQSTM1 Targets Invading Bacteria to the Autophagy Pathway
- Cell death by Autophagy: facts and apparent artefacts
- PAMPs and DAMPs: signal 0s that spur Autophagy and immunity
- Chloroquine in Cancer Therapy: A Double-Edged Sword of Autophagy
- Lysosomal calcium signalling regulates Autophagy through calcineurin and TFEB
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy in protein quality control
- Novel System for Monitoring Autophagy in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Spatial Coupling of mTOR and Autophagy Augments Secretory Phenotypes
- Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet?
- Plant Autophagy—more than a starvation response
- Regulation of Autophagy by the inositol trisphosphate receptor
- Selective degradation of p62 by Autophagy
- Roles of LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 in lysosome biogenesis and Autophagy
- MicroRNA regulation of Autophagy
- Autophagy and Autophagy-related proteins in the immune system
- Loss of Autophagy Diminishes Pancreatic β Cell Mass and Function with Resultant Hyperglycemia
- Autophagy and neurodegeneration
- Apoptosis and Autophagy: regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes
- A critical role for the Autophagy gene Atg5 in T cell survival and proliferation
- Control of Autophagy as a therapy for neurodegenerative disease
- Atg8: an Autophagy-related ubiquitin-like protein family
- Autophagy Controls Salmonella Infection in Response to Damage to the Salmonella-containing Vacuole
- Autophagy and metastasis: another double-edged sword
- Mitochondrial fusion, fission and Autophagy as a quality control axis: The bioenergetic view
- Postfertilization Autophagy of Sperm Organelles Prevents Paternal Mitochondrial DNA Transmission
- Apg7p/Cvt2p: A Novel Protein-activating Enzyme Essential for Autophagy
- Direct Induction of Autophagy by Atg1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptotic Cell Death
- Tor Directly Controls the Atg1 Kinase Complex To Regulate Autophagy
- Bacteria–Autophagy interplay: a battle for survival
- Autophagy in human type 2 diabetes pancreatic beta cells
- Autophagy, Metabolism, and Cancer
- Molecular definitions of Autophagy and related processes
- Autophagy genes and ageing
- Autophagy–physiology and pathophysiology
- Protective role of Autophagy in neonatal hypoxia–ischemia induced brain injury
- Neuronal Autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases
- Phosphorylation of p62 Activates the Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway during Selective Autophagy
- Autophagy in Antimicrobial Immunity
- Induction of Autophagy in Axonal Dystrophy and Degeneration
- Autophagy influences glomerular disease susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice
- The role of Autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease
- Coronavirus Replication Complex Formation Utilizes Components of Cellular Autophagy
- The Autophagy effector Beclin 1: a novel BH3-only protein
- The Autophagy machinery is required to initiate hepatitis C virus replication
- Autophagy in tumour suppression and promotion
- Bcl-2 Inhibition of Autophagy: A New Route to Cancer?
- ESCRTs and Fab1 Regulate Distinct Steps of Autophagy
- FOXO3A directs a protective Autophagy program in haematopoietic stem cells
- Atg8‐family interacting motif crucial for selective Autophagy
- p53 status determines the role of Autophagy in pancreatic tumour development
- DNA damage and Autophagy
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy: selectivity pays off
- Autophagy
- Autophagy Reduces Acute Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Steatosis in Mice
- microRNA‐101 is a potent inhibitor of Autophagy
- Nutrient-sensing nuclear receptors coordinate Autophagy
- A Role for Autophagy in the Extension of Lifespan by Dietary Restriction in C. elegans
- Inhibition of Autophagy Prevents Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron Death after Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury
- Cytoplasmic bacteria can be targets for Autophagy
- The multiple roles of Autophagy in cancer
- Autophagy is a therapeutic target in anticancer drug resistance
- Regulation of the aging process by Autophagy
- Autophagy and cell death in model organisms
- The Autophagy protein Atg7 is essential for hematopoietic stem cell maintenance
- Autophagy Is Essential for Mitochondrial Clearance in Mature T Lymphocytes
- Image-based genome-wide siRNA screen identifies selective Autophagy factors
- Autophagy and Cancer Therapy
- PpAtg30 Tags Peroxisomes for Turnover by Selective Autophagy
- Absence of Autophagy results in reactive oxygen species-dependent amplification of RLR signaling
- Autophagy and human disease: emerging themes
- Regulation of Autophagy by Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Implications for Cancer Progression and Treatment
- Chemical modulators of Autophagy as biological probes and potential therapeutics
- Pathophysiology of chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum turnover by selective Autophagy
- Autosis and autophagic cell death: the dark side of Autophagy
- The Role of Autophagy in Mammalian Development: Cell Makeover Rather than Cell Death
- Regulation of the Autophagy protein LC3 by phosphorylation
- Therapeutic targets in cancer cell metabolism and Autophagy
- Autophagy: Pathways for Self-Eating in Plant Cells
- An Autophagy–Enhancing Drug Promotes Degradation of Mutant α1-Antitrypsin Z and Reduces Hepatic Fibrosis
- Autophagy Regulates Cholesterol Efflux from Macrophage Foam Cells via Lysosomal Acid Lipase
- Mechanisms of Selective Autophagy
- Mechanisms of cross‐talk between the ubiquitin‐proteasome and Autophagy‐lysosome systems
- Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy
- A novel assay to study Autophagy: regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino acid deprivation
- Coordination of membrane events during Autophagy by multiple class III PI3-kinase complexes
- Molecular mechanism and regulation of Autophagy
- Induction of Autophagy by amino-acid deprivation in perfused rat liver
- Modulation of intracellular ROS levels by TIGAR controls Autophagy
- Mechanisms of Autophagy
- Cross talk between apoptosis and Autophagy by caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin 1
- Autophagy Protects against Sindbis Virus Infection of the Central Nervous System
- Degradation of Oxidized Proteins by Autophagy during Oxidative Stress in Arabidopsis
- The Autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid β accumulation in mice
- Autophagy in immunity and cell‐autonomous defense against intracellular microbes
- The Reversible Modification Regulates the Membrane-Binding State of Apg8/Aut7 Essential for Autophagy and the Cytoplasm to Vacuole Targeting Pathway
- Overexpression of Atg5 in mice activates Autophagy and extends lifespan
- TAK1 activates AMPK‐dependent cytoprotective Autophagy in TRAIL‐treated epithelial cells
- Autophagy in thymic epithelium shapes the T-cell repertoire and is essential for tolerance
- Integration of Clearance Mechanisms: The Proteasome and Autophagy
- Role of Autophagy in suppression of inflammation and cancer
- Autophagy is an immediate macrophage response to Legionella pneumophila
- Stimulation of Autophagy by the p53 target gene Sestrin2
- Functional interaction between Autophagy and ciliogenesis
- Role of mitochondrial permeability transition pores in mitochondrial Autophagy
- Autophagy: An Emerging Immunological Paradigm
- MyD88 and Trif Target Beclin 1 to Trigger Autophagy in Macrophages
- The eIF2α/ATF4 pathway is essential for stress-induced Autophagy gene expression
- Ubiquitin-Dependent And Independent Signals In Selective Autophagy
- UPR, Autophagy, and mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response
- Regulation of Neuronal Survival Factor MEF2D by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy
- Autophagy in Huntington disease and huntingtin in Autophagy
- Selective Autophagy in Cancer Development and Therapy
- Signalling and Autophagy regulation in health, aging and disease
- Autophagy in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors attenuate cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing Autophagy
- Extracellular matrix regulation of Autophagy
- HMGB1 release and redox regulates Autophagy and apoptosis in cancer cells
- Autophagy in the cardiovascular system
- Crosstalk Between Autophagy and Apoptosis in Heart Disease
- The anticancer drug imatinib induces cellular Autophagy
- Complex Inhibitory Effects of Nitric Oxide on Autophagy
- Initiation of apoptosis and Autophagy by photodynamic therapy
- Autophagy mediates degradation of nuclear lamina
- Role of LAMP-2 in Lysosome Biogenesis and Autophagy
- NBR1 and p62 as cargo receptors for selective Autophagy of ubiquitinated targets
- Mature ribosomes are selectively degraded upon starvation by an Autophagy pathway requiring the Ubp3p/Bre5p ubiquitin protease
- Linking of Autophagy to Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Is Important for the Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Cell Viability
- Autophagy and cancer cell metabolism
- TFEB-mediated Autophagy rescues midbrain dopamine neurons from α-synuclein toxicity
- Crosstalk between apoptosis and Autophagy within the Beclin 1 interactome
- Autophagy negatively regulates Wnt signalling by promoting Dishevelled degradation
- Activation of Autophagy protects against acetaminophen‐induced hepatotoxicity
- Enhanced Autophagy ameliorates cardiac proteinopathy
- Following Autophagy step by step
- Akt inhibition promotes Autophagy and sensitizes PTEN-null tumors to lysosomotropic agents
- Autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system: Collaborators in neuroprotection
- Restoration of chaperone-mediated Autophagy in aging liver improves cellular maintenance and hepatic function
- Autophagy in cardiovascular disease
- Canonical and non-canonical Autophagy: variations on a common theme of self-eating?
- Approaching the Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy
- Does Autophagy have a license to kill mammalian cells?
- Egr-1 Regulates Autophagy in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Generation of cell lines with tetracycline‐regulated Autophagy and a role for Autophagy in controlling cell size
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy at a glance
- Efficient Cross-presentation Depends on Autophagy in Tumor Cells
- Autophagy: Regulation and role in disease
- Atg17 Functions in Cooperation with Atg1 and Atg13 in Yeast Autophagy
- Autophagy in cardiac myocyte homeostasis, aging, and pathology
- Autophagy, Cytoplasm-to-Vacuole Targeting Pathway, and Pexophagy in Yeast and Mammalian Cells
- Autophagy Is Activated by Apoptotic Signalling in Sympathetic Neurons: An Alternative Mechanism of Death Execution
- A Noncanonical Mechanism of Nrf2 Activation by Autophagy Deficiency: Direct Interaction between Keap1 and p62
- TBK-1 Promotes Autophagy–Mediated Antimicrobial Defense by Controlling Autophagosome Maturation
- Role of Autophagy in G2019S‐LRRK2‐associated neurite shortening in differentiated SH‐SY5Y cells
- Autophagy-mediated reentry of Francisella tularensis into the endocytic compartment after cytoplasmic replication
- Ammonia-induced Autophagy is independent of ULK1/ULK2 kinases
- Autophagy, a guardian against neurodegeneration
- Autophagy Contributes to Caspase-independent Macrophage Cell Death
- Autophagy Is Important in Islet Homeostasis and Compensatory Increase of Beta Cell Mass in Response to High-Fat Diet
- Autophagy in cardiovascular biology
- Autophagy: machinery and regulation
- Mammalian Autophagy: How Does It Work?
- Autophagy requires endoplasmic reticulum targeting of the PI3-kinase complex via Atg14L
- Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute kidney injury
- Differential Regulation of Distinct Vps34 Complexes by AMPK in Nutrient Stress and Autophagy
- Aggresomes and Autophagy Generate Sites for Virus Replication
- Autophagy pathway intersects with HIV-1 biosynthesis and regulates viral yields in macrophages
- Autophagy and adaptive immunity
- Synergistic Augmentation of Rapamycin-Induced Autophagy in Malignant Glioma Cells by Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Inhibitors
- Postischemic treatment of neonatal cerebral ischemia should target Autophagy
- Autophagy-mediated clearance of huntingtin aggregates triggered by the insulin-signaling pathway
- p65/RelA Modulates BECN1 Transcription and Autophagy
- Autophagy in health and disease. 1. Regulation and significance of Autophagy: an overview
- Plasma cells require Autophagy for sustainable immunoglobulin production
- Tissue-specific Autophagy Alterations and Increased Tumorigenesis in Mice Deficient in Atg4C/Autophagin-3
- Glucocorticoid‐induced Autophagy in osteocytes
- An Atg1/Atg13 Complex with Multiple Roles in TOR-mediated Autophagy Regulation
- Eating the endoplasmic reticulum: quality control by Autophagy
- Differential Regulation of Caspase-1 Activation, Pyroptosis, and Autophagy via Ipaf and ASC in Shigella-Infected Macrophages
- siRNA Screening of the Kinome Identifies ULK1 as a Multidomain Modulator of Autophagy
- Autophagy and Tumorigenesis
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy: Molecular mechanisms and physiological relevance
- Cytosolic FoxO1 is essential for the induction of Autophagy and tumour suppressor activity
- Extracellular M. tuberculosis DNA Targets Bacteria for Autophagy by Activating the Host DNA-Sensing Pathway
- Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces severity of experimental osteoarthritis
- A New Protein Conjugation System in Human
THE COUNTERPART OF THE YEAST Apg12p CONJUGATION SYSTEM ESSENTIAL FOR Autophagy - Role of Mitochondrial Inner Membrane Permeabilization in Necrotic Cell Death, Apoptosis, and Autophagy
- Mutant p53 protein localized in the cytoplasm inhibits Autophagy
- SIRT1: Regulation of longevity via Autophagy
- Autophagy, Not Apoptosis, Is Essential for Midgut Cell Death in Drosophila
- Regulation of Autophagy by mTOR-dependent and mTOR-independent pathways: Autophagy dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic application of Autophagy enhancers
- Eukaryotic Stress Granules Are Cleared by Autophagy and Cdc48/VCP Function
- Linking ER Stress to Autophagy: Potential Implications for Cancer Therapy
- Control of Autophagy initiation by phosphoinositide 3‐phosphatase jumpy
- Degradation of Paternal Mitochondria by Fertilization-Triggered Autophagy in C. elegans Embryos
- How to Live Long and Prosper: Autophagy, Mitochondria, and Aging
- Autophagy Is an Essential Component of Drosophila Immunity against Vesicular Stomatitis Virus
- Autophagy inhibitor Lys05 has single-agent antitumor activity and reproduces the phenotype of a genetic Autophagy deficiency
- Autophagy enhances the efficacy of BCG vaccine by increasing peptide presentation in mouse dendritic cells
- Rapamycin protects against rotenone-induced apoptosis through Autophagy induction
- Proteases in Autophagy
- Adipose-specific deletion of Autophagy-related gene 7 (atg7) in mice reveals a role in adipogenesis
- The Four Faces of Autophagy: Implications for Cancer Therapy
- Lysosomal killing of Mycobacterium mediated by ubiquitin-derived peptides is enhanced by Autophagy
- Autophagy Signaling Through Reactive Oxygen Species
- PARTICIPATION OF LYSOSOMES IN CELLULAR Autophagy INDUCED IN RAT LIVER BY GLUCAGON
- Autophagy for tissue homeostasis and neuroprotection
- Molecules and their functions in Autophagy
- Aβ Secretion and Plaque Formation Depend on Autophagy
- Structural basis of target recognition by Atg8/LC3 during selective Autophagy
- Autophagy is defective in collagen VI muscular dystrophies, and its reactivation rescues myofiber degeneration
- Metformin inhibits melanoma development through Autophagy and apoptosis mechanisms
- Altered Autophagy in Human Adipose Tissues in Obesity
- Autophagy protects against active tuberculosis by suppressing bacterial burden and inflammation
- Aggregate‐Prone Proteins Are Cleared from the Cytosol by Autophagy: Therapeutic Implications
- MicroRNAs in apoptosis, Autophagy and necroptosis
- Relationship between the proteasomal system and Autophagy
- Rapamycin and mTOR-independent Autophagy inducers ameliorate toxicity of polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin and related proteinopathies
- Autophagy Induction by the Pathogen Receptor CD46
- PUMA- and Bax-induced Autophagy contributes to apoptosis
- Autophagy Proteins Regulate the Secretory Component of Osteoclastic Bone Resorption
- mTORC1 Phosphorylates the ULK1-mAtg13-FIP200 Autophagy Regulatory Complex
- Eating the enemy within: Autophagy in infectious diseases
- INFLUENCE OF GLUCAGON, AN INDUCER OF CELLULAR Autophagy, ON SOME PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF RAT LIVER LYSOSOMES
- Downregulated MEG3 activates Autophagy and increases cell proliferation in bladder cancer
- Distinct Autophagosomal-Lysosomal Fusion Mechanism Revealed by Thapsigargin-Induced Autophagy Arrest
- Regulation of Autophagy by the p300 Acetyltransferase
- GAPDH and Autophagy Preserve Survival after Apoptotic Cytochrome c Release in the Absence of Caspase Activation
- Keap1 degradation by Autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis
- Viruses and the Autophagy machinery
- Autophagy: molecular mechanisms, physiological functions and relevance in human pathology
- Essential role for Autophagy in life span extension
- Targeting Autophagy Addiction in Cancer
- p62, an Autophagy hero or culprit?
- Autophagy in Yeast: ATOR-Mediated Response to Nutrient Starvation
- The Legionella Effector RavZ Inhibits Host Autophagy Through Irreversible Atg8 Deconjugation
- BNIP3 Is an RB/E2F Target Gene Required for Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy
- The unfolded protein response protects human tumor cells during hypoxia through regulation of the Autophagy genes MAP1LC3B and ATG5
- p53/HMGB1 Complexes Regulate Autophagy and Apoptosis
- The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian Autophagy
- Valosin-containing protein (VCP) is required for Autophagy and is disrupted in VCP disease
- Autophagy in Load-Induced Heart Disease
- To Be or Not to Be? How Selective Autophagy and Cell Death Govern Cell Fate
- Wild Type α-Synuclein Is Degraded by Chaperone-mediated Autophagy and MacroAutophagy in Neuronal Cells
- Protein breakdown in muscle wasting: Role of Autophagy-lysosome and ubiquitin-proteasome
- Autophagy deficiency leads to protection from obesity and insulin resistance by inducing Fgf21 as a mitokine
- How do ESCRT proteins control Autophagy?
- Resveratrol-Activated AMPK/SIRT1/Autophagy in Cellular Models of Parkinson’s Disease
- Autophagy: a multifaceted intracellular system for bulk and selective recycling
- Autophagy promotes synapse development in Drosophila
- Autophagy, proteasomes, lipofuscin, and oxidative stress in the aging brain
- Spermidine and resveratrol induce Autophagy by distinct pathways converging on the acetylproteome
- Noncanonical Autophagy Promotes the Visual Cycle
- Regulation of Autophagy by ATF4 in response to severe hypoxia
- C. elegans Screen Identifies Autophagy Genes Specific to Multicellular Organisms
- Chapter 10 Monitoring Autophagy by Electron Microscopy in Mammalian Cells
- Glycogen Autophagy in glucose homeostasis
- mTOR inhibits Autophagy by controlling ULK1 ubiquitylation, self-association and function through AMBRA1 and TRAF6
- The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte Autophagy
- XBP-1 deficiency in the nervous system protects against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by increasing Autophagy
- Autophagy in cellular growth control
- Suppression of Autophagy by FIP200 deletion inhibits mammary tumorigenesis
- AMPK and Autophagy get connected
- Processing of ATG8s, Ubiquitin-Like Proteins, and Their Deconjugation by ATG4s Are Essential for Plant Autophagy
- Regulation of Autophagy by Cytosolic Acetyl-Coenzyme A
- Transcriptional control of Autophagy–lysosome function drives pancreatic cancer metabolism
- Impaired Autophagy of an Intracellular Pathogen Induced by a Crohn’s Disease Associated ATG16L1 Variant
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibition of phagolysosome biogenesis and Autophagy as a host defence mechanism
- The return of the nucleus: transcriptional and epigenetic control of Autophagy
- Autophagy and disease: always two sides to a problem
- Early endosomes and endosomal coatomer are required for Autophagy
- A role for Autophagy during hepatic stellate cell activation
- Autophagy in Yeast: Mechanistic Insights and Physiological Function
- Apg16p is required for the function of the Apg12p–Apg5p conjugate in the yeast Autophagy pathway
- Nonselective Autophagy of cytosolic enzymes by isolated rat hepatocytes.
- Autophagy Is Required for Maintenance of Amino Acid Levels and Protein Synthesis under Nitrogen Starvation
- Dual Role of 3-Methyladenine in Modulation of Autophagy via Different Temporal Patterns of Inhibition on Class I and III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase
- Identification of Barkor as a mammalian Autophagy-specific factor for Beclin 1 and class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- HDACs link the DNA damage response, processing of double-strand breaks and Autophagy
- Autophagy and Cancer
- Autophagy—a key player in cellular and body metabolism
- Sirtuins’ modulation of Autophagy
- Tumor Vessel Normalization by Chloroquine Independent of Autophagy
- Autophagy and Neurodegeneration: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities
- Autophagy in neurodegeneration and development
- The Cvt pathway as a model for selective Autophagy
- Autophagy is involved in T cell death after binding of HIV-1 envelope proteins to CXCR4
- Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy Promotes Tumor Cell Survival and Adaptation to Antiangiogenic Treatment in Glioblastoma
- Regulation of Autophagy by Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinases During 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium-Induced Cell Death
- Autophagy Protects the Proximal Tubule from Degeneration and Acute Ischemic Injury
- Autophagy: links with the proteasome
- The crosstalk between Autophagy and apoptosis: where does this lead?
- Autophagy Protects the Proximal Tubule from Degeneration and Acute Ischemic Injury
- The tumor suppressor gene ARHI regulates Autophagy and tumor dormancy in human ovarian cancer cells
- Autophagy and Tumor Metabolism
- Essential role for Autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration
- Autophagy in Protein and Organelle Turnover
- Sphingolipids: regulators of crosstalk between apoptosis and Autophagy
- HMGB1-induced Autophagy promotes chemotherapy resistance in leukemia cells
- Regulation of Autophagy by phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate
- Focal cerebral ischemia induces upregulation of Beclin 1 and Autophagy–like cell death
- Programmed Autophagy in the Drosophila Fat Body Is Induced by Ecdysone through Regulation of the PI3K Pathway
- Akt and Autophagy Cooperate to Promote Survival of Drug-Resistant Glioma
- Autophagy in filamentous fungi
- Intracellular Protein Aggregation Is a Proximal Trigger of Cardiomyocyte Autophagy
- Regulation of innate immune responses by Autophagy-related proteins
- Participation of Autophagy in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury
- Ubiquilin functions in Autophagy and is degraded by chaperone-mediated Autophagy
- Structural Aspects of Autophagy
- Chapter 1 Monitoring Autophagy in Mammalian Cultured Cells through the Dynamics of LC3
- Ammonia Derived from Glutaminolysis Is a Diffusible Regulator of Autophagy
- Autophagy proteins regulate ERK phosphorylation
- Autophagy in cancer metastasis
- GSK3-TIP60-ULK1 Signaling Pathway Links Growth Factor Deprivation to Autophagy
- Autophagy is cytoprotective during cisplatin injury of renal proximal tubular cells
- Targeting Autophagy potentiates tyrosine kinase inhibitor–induced cell death in Philadelphia chromosome–positive cells, including primary CML stem cells
- Function and Molecular Mechanism of Acetylation in Autophagy Regulation
- Digesting the Expanding Mechanisms of Autophagy
- Autophagy—A double‐edged sword in oncology
- The dual role of Autophagy in cancer
- Emerging Role for Autophagy in the Removal of Aggresomes in Schwann Cells
- A Salmonella protein causes macrophage cell death by inducing Autophagy
- Recycle or die: The role of Autophagy in cardioprotection
- Autophagy in Atherosclerosis
- Autophagy is an adaptive response in desmin-related cardiomyopathy
- Autophagy in Diabetic Nephropathy
- Major histocompatibility complex class II‐restricted presentation of a cytosolic antigen by Autophagy
- Autophagy Is Activated in Colorectal Cancer Cells and Contributes to the Tolerance to Nutrient Deprivation
- Autophagosome-Independent Essential Function for the Autophagy Protein Atg5 in Cellular Immunity to Intracellular Pathogens
- Autophagy enhances the presentation of endogenous viral antigens on MHC class I molecules during HSV-1 infection
- Autophagy in Vascular Disease
- Targeting Autophagy augments the anticancer activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA to overcome Bcr-Abl–mediated drug resistance
- Calorie restriction enhances cell adaptation to hypoxia through Sirt1-dependent mitochondrial Autophagy in mouse aged kidney
- Autophagy contributes to resistance of tumor cells to ionizing radiation
- EGFR-Mediated Beclin 1 Phosphorylation in Autophagy Suppression, Tumor Progression, and Tumor Chemoresistance
- Development of Autophagy inducers in clinical medicine
- Role of Autophagy in Cancer Prevention
- Methamphetamine-Induced Degeneration of Dopaminergic Neurons Involves Autophagy and Upregulation of Dopamine Synthesis
- Peroxisome turnover by micropexophagy: an Autophagy-related process
- In Situ Detection of Starvation-induced Autophagy
- Autophagy in Hypothalamic AgRP Neurons Regulates Food Intake and Energy Balance
- Bcl-2:Beclin 1 complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating Autophagy/apoptosis toggle switch
- Receptor-mediated selective Autophagy degrades the endoplasmic reticulum and the nucleus
- Diet, Autophagy, and Cancer: A Review
- A dual role for Ca2+ in Autophagy regulation
- Autophagy and antiviral immunity
- p62/SQSTM1 functions as a signaling hub and an Autophagy adaptor
- Deacetylation of FoxO by Sirt1 Plays an Essential Role in Mediating Starvation-Induced Autophagy in Cardiac Myocytes
- Protein and mRNA expression of Autophagy gene Beclin 1 in human brain tumours
- Methods for Assessing Autophagy and Autophagic Cell Death
- Constitutive Activation of Chaperone-mediated Autophagy in Cells with Impaired MacroAutophagy
- Regulation of lipid droplets by Autophagy
- Autophagy in cardiac myocytes.
- Membrane Recruitment of Aut7p in the Autophagy and Cytoplasm to Vacuole Targeting Pathways Requires Aut1p, Aut2p, and the Autophagy Conjugation Complex
- Increased Autophagy in transgenic mice with a G93A mutant SOD1 gene
- p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and Autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents
- Huntington’s disease: degradation of mutant huntingtin by Autophagy
- Autophagy modulation for cancer therapy
- Atg5: more than an Autophagy factor
- Apoptosis and Autophagy: Targeting Autophagy signallingin cancer cells – ‘trick or treats’?
- DAP‐kinase‐mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl‐XL and induction of Autophagy
- Negative regulation of Autophagy
- Screen for Chemical Modulators of Autophagy Reveals Novel Therapeutic Inhibitors of mTORC1 Signaling
- Journal of the American College of Cardiology
- Autophagy regulates TNFα-mediated joint destruction in experimental arthritis
- Cholesterol depletion induces Autophagy
- Autophagy mediates pharmacological lifespan extension by spermidine and resveratrol
- Remodeling the Endoplasmic Reticulum by Poliovirus Infection and by Individual Viral Proteins: an Autophagy-Like Origin for Virus-Induced Vesicles
- Neuroprotection of rapamycin in lactacystin-induced neurodegeneration via Autophagy enhancement
- Genetic and Phenotypic Overlap between Autophagy and the Cytoplasm to Vacuole Protein Targeting Pathway
- JNK regulates FoxO-dependent Autophagy in neurons
- Deacetylation of Nuclear LC3 Drives Autophagy Initiation under Starvation
- DNA damaging agent-induced Autophagy produces a cytoprotective adenosine triphosphate surge in malignant glioma cells
- Autophagy, plant senescence, and nutrient recycling
- Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring Autophagy
- p62 links Autophagy and Nrf2 signaling
- Non‐autophagic roles of Autophagy‐related proteins
- Autophagy in atherosclerosis
- Autophagy and pancreatitis
- Radiation-induced Autophagy is associated with LC3 and its inhibition sensitizes malignant glioma cells
- Dual roles of Autophagy in the survival of Caenorhabditis elegans during starvation
- Transcriptional regulation of Autophagy by an FXR–CREB axis
- Autophagy and neurodegeneration
- Autophagy Plays a Role in Chloroplast Degradation during Senescence in Individually Darkened Leaves
- Structure of Atg5·Atg16, a Complex Essential for Autophagy
- Autophagy in tumorigenesis and energy metabolism: friend by day, foe by night
- mTOR and Autophagy: A dynamic relationship governed by nutrients and energy
- TOR-dependent control of Autophagy: biting the hand that feeds
- Starving Neurons Show Sex Difference in Autophagy
- Targeting ER stress–induced Autophagy overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma
- Starvation‐induced expression of Autophagy‐related genes in Arabidopsis
- Involvement of Autophagy in trypsinogen activation within the pancreatic acinar cells
- ROS and Autophagy: Interactions and Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms
- The Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Receptor Organizes in Dynamic Protein Complexes at the Lysosomal Membrane
- BAG3 mediates chaperone‐based aggresome‐targeting and selective Autophagy of misfolded proteins
- The Role of Lipids in the Control of Autophagy
- mTOR’s role in ageing: protein synthesis or Autophagy?
- Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1a Growth and Induction of Autophagy
- Selective types of Autophagy in yeast
- The Parkinson-associated protein PINK1 interacts with Beclin1 and promotes Autophagy
- Regulation of Autophagy by the Rab GTPase network
- Autophagy suppresses progression of K-ras-induced lung tumors to oncocytomas and maintains lipid homeostasis
- Bcl‐2 and Bcl‐xL play important roles in the crosstalk between Autophagy and apoptosis
- Autophagy as an essential cellular antioxidant pathway in neurodegenerative disease
- Autophagy Releases Lipid That Promotes Fibrogenesis by Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells in Mice and in Human Tissues
- Inhibition of Autophagy in Mitotic Animal Cells
- Crohn’s disease: NOD2, Autophagy and ER stress converge
- Autophagy and inflammatory diseases
- Autophagy
- Regulation of Autophagy by stress-responsive transcription factors
- Dengue Virus and Autophagy
- Analyses of APG13 gene involved in Autophagy in yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- The Impact of Autophagy on Cell Death Modalities
- Regulation of Autophagy in mammals and its interplay with apoptosis
- Aging: Central role for Autophagy and the lysosomal degradative system
- Autophagy and the degradation of mitochondria
- Dependence of hepatocytic Autophagy on intracellularly sequestered calcium.
- Autophagy in Innate Immunity against Intracellular Bacteria
- Autophagy: Role in surviving environmental stress
- Autophagy: Is It Cancer’s Friend or Foe?
- Autophagy and Its Role in MHC-Mediated Antigen Presentation
- Autophagy and genomic integrity
- Autophagy induction favours the generation and maturation of the Coxiella‐replicative vacuoles
- Autophagy and p62 in Cardiac Proteinopathy
- Ordered Organelle Degradation during Starvation-induced Autophagy
- Autophagy, Inflammation, and Immunity: A Troika Governing Cancer and Its Treatment
- AMPK-Dependent Phosphorylation of ULK1 Induces Autophagy
- Autophagy: shaping the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response
- Autophagy in the Lung
- Autophagy and antigen presentation
- Atg7-dependent Autophagy promotes neuronal health, stress tolerance, and longevity but is dispensable for metamorphosis in Drosophil
- DJ-1 acts in parallel to the PINK1/parkin pathway to control mitochondrial function and Autophagy
- The induction of Autophagy by γ‐radiation contributes to the radioresistance of glioma stem cells
- Apoptosis and Autophagy: Regulation of caspase‐9 by phosphorylation
- TRAF6 and A20 Regulate Lysine 63–Linked Ubiquitination of Beclin-1 to Control TLR4-Induced Autophagy
- Autophagy regulation and its role in cancer
- Role of non-canonical Beclin 1-independent Autophagy in cell death induced by resveratrol in human breast cancer cells
- Methods for detecting Autophagy and determining Autophagy–induced cell death
- Formation of the ∼350-kDa Apg12-Apg5·Apg16 Multimeric Complex, Mediated by Apg16 Oligomerization, Is Essential for Autophagy in Yeast
- Autophagy in neurodegenerative disorders: pathogenic roles and therapeutic implications
- ER stress–mediated Autophagy promotes Myc-dependent transformation and tumor growth
- AMPK‐mediated Autophagy inhibits apoptosis in cisplatin‐treated tumour cells
- Atg22 Recycles Amino Acids to Link the Degradative and Recycling Functions of Autophagy
- Autophagy Induced by Ischemic Preconditioning is Essential for Cardioprotection
- Autophagy machinery mediates macroendocytic processing and entotic cell death by targeting single membranes
- Autophagy as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease
- Proteasome inhibitors activate Autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human prostate cancer cells
- Induction of Autophagy Promotes Fusion of Multivesicular Bodies with Autophagic Vacuoles in K562 Cells
- Oxidative Stress, Redox Signaling, and Autophagy: Cell Death Versus Survival
- A Non-canonical MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway Regulates Autophagy via Regulating Beclin 1
- Alpha-alumina nanoparticles induce efficient Autophagy-dependent cross-presentation and potent antitumour response
- Application and interpretation of current Autophagy inhibitors and activators
- Modification of Cellular Autophagy Protein LC3 by Poliovirus
- Inactivation of the Autophagy Gene bec-1 Triggers Apoptotic Cell Death in C. elegans
- Autophagy in cellular metabolism and cancer
- Autophagy as a Stress-Response and Quality-Control Mechanism: Implications for Cell Injury and Human Disease
- Autophagy Is Required for Glucose Homeostasis and Lung Tumor Maintenance
- Induction of ROS, mitochondrial damage and Autophagy in lung epithelial cancer cells by iron oxide nanoparticles
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy in health and disease
- Autophagy in health and disease. 3. Involvement of Autophagy in muscle atrophy
- Oxidative stress and Autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and cancer
- Selective types of Autophagy
- Selective Autophagy
- Autophagy is required for necrotic cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans
- Dopamine Oxidation and Autophagy
- Autophagy: Paying Charon’s Toll
- Self and Nonself: How Autophagy Targets Mitochondria and Bacteria
- Autophagy as a cell-repair mechanism: Activation of chaperone-mediated Autophagy during oxidative stress
- Mutant A53T α-Synuclein Induces Neuronal Death by Increasing Mitochondrial Autophagy
- Connections between SNAREs and Autophagy
- Emerging strategies to effectively target Autophagy in cancer
- Pharmacological modulation of Autophagy: therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles
- Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring Autophagy in higher eukaryotes
- The endoplasmic reticulum in apoptosis and Autophagy: role of the BCL-2 protein family
- Autophagy, polyphenols and healthy ageing
- Autophagy in neuroprotection and neurodegeneration: a question of balance
- Trs85 directs a Ypt1 GEF, TRAPPIII, to the phagophore to promote Autophagy
- Hypoxia signals Autophagy in tumor cells via AMPK activity, independent of HIF-1, BNIP3, and BNIP3L
- The role of autophagy in tumour development and cancer therapy
- Autophagy in cutaneous malignant melanoma
- Sulforaphane Causes Autophagy to Inhibit Release of Cytochrome c and Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells
- Ceramides and other bioactive sphingolipid backbones in health and disease: Lipidomic analysis, metabolism and roles in membrane structure, dynamics, signaling and Autophagy
- Toll-like receptors in control of immunological Autophagy
- Protein Kinase A and Sch9 Cooperatively Regulate Induction of Autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Selective Autophagy in budding yeast
- Class III PI3K Vps34 plays an essential role in Autophagy and in heart and liver function
- Small molecule enhancers of Autophagy for neurodegenerative diseases
- Acetylation Targets the M2 Isoform of Pyruvate Kinase for Degradation through Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy and Promotes Tumor Growth
- Autophagy and mitophagy in cellular damage control
- Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy
- Organelle-Specific Initiation of Autophagy
- Caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin-1 inactivates Beclin-1-induced Autophagy and enhances apoptosis by promoting the release of proapoptotic factors from mitochondria
- Autophagy in Drosophila melanogaster
- Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring Autophagy (3rd edition)
- Membrane Origin for Autophagy
- Autophagy as an innate immunity paradigm: expanding the scope and repertoire of pattern recognition receptors
- Association of Autophagy Defect with a Malignant Phenotype and Poor Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Dynamic and transient interactions of Atg9 with autophagosomes, but not membrane integration, are required for Autophagy
- Toward unraveling membrane biogenesis in mammalian Autophagy
- Mechanisms of Autophagy Initiation
- All-you-can-eat: Autophagy in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection
- A Novel Protein Complex Linking the δ2 Glutamate Receptor and Autophagy: Implications for Neurodegeneration in Lurcher Mice
- Apg9p/Cvt7p Is an Integral Membrane Protein Required for Transport Vesicle Formation in the Cvt and Autophagy Pathways
- Apg14p and Apg6/Vps30p Form a Protein Complex Essential for Autophagy in the Yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- The class III PI(3)K Vps34 promotes Autophagy and endocytosis but not TOR signaling in Drosophila
- Life, death and burial: multifaceted impact of Autophagy
- Glycogen Autophagy
- Autophagy in human tumors: cell survival or death?
- Quantum Dots for Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeling. A Size-Dependent Autophagy Activation
- Autophagy and cancer – issues we need to digest
- Feedback on Fat: p62-mTORC1-Autophagy Connections
- Monitoring and Measuring Autophagy
- Nutrient-dependent regulation of Autophagy through the target of rapamycin pathway
- Neuronal Autophagy in experimental scrapie
- Autophagy promotes necrosis in apoptosis-deficient cells in response to ER stress
- Abberant α-Synuclein Confers Toxicity to Neurons in Part through Inhibition of Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy
- Human IRGM regulates Autophagy and cell-autonomous immunity functions through mitochondria
- Role of the Apg12 conjugation system in mammalian Autophagy
- Autophagy in C. elegans
- Prorenin Receptor Is Essential for Podocyte Autophagy and Survival
- Autophagy after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- ZKSCAN3 Is a Master Transcriptional Repressor of Autophagy
- Autophagy, Apoptosis, Mitoptosis and Necrosis: Interdependence Between Those Pathways and Effects on Cancer
- Nix Is Critical to Two Distinct Phases of Mitophagy, Reactive Oxygen Species-mediated Autophagy Induction and Parkin-Ubiquitin-p62-mediated Mitochondrial Priming
- Targeting Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases
- Identification of Regulators of Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy
- Runx1 prevents wasting, myofibrillar disorganization, and Autophagy of skeletal muscle
- Autophagy and cell death
- Autophagy in aging, disease and death: the true identity of a cell death impostor
- Autophagy Contributes to Leaf Starch Degradation
- Targeting Autophagy during cancer therapy to improve clinical outcomes
- Autophagy: More Than a Nonselective Pathway
- Immunologic manifestations of Autophagy
- Azithromycin blocks Autophagy and may predispose cystic fibrosis patients to mycobacterial infection
- Cellular and metabolic functions for Autophagy in cancer cells
- Autophagy as a pro‐death pathway
- Mitochondria regulate Autophagy by conserved signalling pathways
- Autophagy in Vascular Disease
- Autophagy: a druggable process that is deregulated in aging and human disease
- The regulation of aging: does Autophagy underlie longevity?
- Turnover of organelles by Autophagy in yeast
- Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal cartilage, and its aging‐related loss is linked with cell death and osteoarthritis
- Cleaning House: Selective Autophagy of Organelles
- Therapeutic Targeting of Autophagy
- Interactions of Pathogenic Bacteria with Autophagy Systems
- PLIC proteins or ubiquilins regulate Autophagy‐dependent cell survival during nutrient starvation
- Autophagy proteins in macroendocytic engulfment
- Constitutive Autophagy: vital role in clearance of unfavorable proteins in neurons
- Endocytosis and Autophagy: Shared machinery for degradation
- Autophagy regulates selective HMGB1 release in tumor cells that are destined to die
- Autophagy in organelle homeostasis: Peroxisome turnover
- Regulation of Autophagy in human and murine cartilage: Hypoxia‐inducible factor 2 suppresses chondrocyte Autophagy
- Inhibition of Autophagy abrogates tumour necrosis factor α induced apoptosis in human T‐lymphoblastic leukaemic cells
- Autophagy as a target for cancer therapy: new developments
- Hypoxia-activated Autophagy accelerates degradation of SQSTM1/p62
- The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of Autophagy and the clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration
- Autophagy genes protect against Salmonella typhimurium infection and mediate insulin signaling-regulated pathogen resistance
- The molecular mechanism of mitochondria Autophagy in yeast
- Reversal of Autophagy dysfunction in the TgCRND8 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease ameliorates amyloid pathologies and memory deficits
- Induction of Autophagy is essential for monocyte-macrophage differentiation
- Autophagy takes flight inDrosophila
- Chapter 2 Methods for Monitoring Autophagy Using GFP‐LC3 Transgenic Mice
- Induction of Autophagy-dependent necroptosis is required for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to overcome glucocorticoid resistance
- Autophagy Impairment Induces Premature Senescence in Primary Human Fibroblasts
- Autophagy Negatively Regulates Cell Death by Controlling NPR1-Dependent Salicylic Acid Signaling during Senescence and the Innate Immune Response in Arabidopsis
- Autophagy and ethanol-induced liver injury
- Autophagy and mitophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Metabolic Stress in Autophagy and Cell Death Pathways
- Autophagy in disease: a double-edged sword with therapeutic potential
- Autophagy as a mediator of chemotherapy-induced cell death in cancer
- AMPK-independent induction of Autophagy by cytosolic Ca2+ increase
- Autophagy regulates inflammation in adipocytes
- Autophagy: molecular machinery, regulation, and implications for renal pathophysiology
- Expression of beclin‐1, an Autophagy‐related protein, in gastric and colorectal cancers
- CD40 induces macrophage anti–Toxoplasma gondii activity by triggering Autophagy-dependent fusion of pathogen-containing vacuoles and lysosomes
- Autophagy and misfolded proteins in neurodegeneration
- The late stages of Autophagy: how does the end begin?
- Autophagy Regulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis and Calcium Mobilization in T Lymphocytes
- Cadmium-induced Autophagy and apoptosis are mediated by a calcium signaling pathway
- The Role of ATF4 Stabilization and Autophagy in Resistance of Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Bortezomib
- Autophagy and bacterial infectious diseases
- Autophagy in Atherosclerosis
- Autophagy and Viruses: Adversaries or Allies?
- Mitochondrial Autophagy and injury in the liver in α1-antitrypsin deficiency
- TOR Is a Negative Regulator of Autophagy in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Steroid‐triggered death by Autophagy
- Autophagy, the Trojan horse to combat glioblastomas
- Inhibition of Autophagy by 3-MA Enhances the Effect of 5-FU-Induced Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells
- Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is required for induction of Autophagy during lumen formation in vitro
- Endosome Sorting and Autophagy Are Essential for Differentiation and Virulence of Leishmania major
- Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian Autophagy
- Cell death and Autophagy: Cytokines, drugs, and nutritional factors
- Endogenous Drp1 Mediates Mitochondrial Autophagy and Protects the Heart Against Energy Stress
- Quantitative relationship between Autophagy and proteolysis during graded amino acid deprivation in perfused rat liver.
- Organellophagy: Eliminating cellular building blocks via selective Autophagy
- Chapter 3 The Quantitative Pho8Δ60 Assay of Nonspecific Autophagy
- Atomistic Autophagy: The Structures of Cellular Self-Digestion
- The IP3 receptor–mitochondria connection in apoptosis and Autophagy
- Nutrient Sensing, Autophagy, and Diabetic Nephropathy
- Aging and Autophagy in the Heart
- Arginine Deiminase as a Novel Therapy for Prostate Cancer Induces Autophagy and Caspase-Independent Apoptosis
- Autophagy in health and disease. 2. Regulation of lipid metabolism and storage by Autophagy: pathophysiological implications
- Autophagy and cartilage homeostasis mechanisms in joint health, aging and OA
- Autophagy, cell death, and cancer
- Autophagy and endocrine resistance in breast cancer
- Autophagy in MHC class II antigen processing
- At the end of the autophagic road: an emerging understanding of lysosomal functions in Autophagy
- Microtubule-associated Protein 1 Light Chain 3 (LC3) Interacts with Bnip3 Protein to Selectively Remove Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria via Autophagy
- Targeting cancer cells through Autophagy for anticancer therapy
- Autophagy failure in Alzheimer’s disease and the role of defective lysosomal acidification
- Subversion of cellular Autophagy by Anaplasma phagocytophilum
- Autophagy as a new therapeutic target in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Autophagy and viral neurovirulence
- The Role of the Selective Adaptor p62 and Ubiquitin-Like Proteins in Autophagy
- Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 regulates Autophagy through a calcium-dependent pathway involving NAADP
- Autophagy – An Emerging Anti-Aging Mechanism
- Autophagy in Pulmonary Diseases
- Tau degradation: The ubiquitin–proteasome system versus the Autophagy-lysosome system
- Degradation of lipid droplet-associated proteins by chaperone-mediated Autophagy facilitates lipolysis
- Review: Autophagy in neurodegeneration: firefighter and/or incendiarist?
- Chikungunya virus–induced Autophagy delays caspase-dependent cell death
- Autophagy protein microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain-3B (LC3B) activates extrinsic apoptosis during cigarette smoke-induced emphysema
- Accelerated Cell Death in Podospora Autophagy Mutants
- Multiple regulatory and effector roles of Autophagy in immunity
- Chaperone-mediated Autophagy: machinery, regulation and biological consequences
- ANG II promotes Autophagy in podocytes
- Protective Role of Autophagy in Palmitate-Induced INS-1 β-Cell Death
- Midbody ring disposal by Autophagy is a post-abscission event of cytokinesis
- Autophagy in the immune system
- Cardioprotection by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress–Induced Autophagy
- MiR-30-Regulated Autophagy Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Myocardial Hypertrophy
- Chapter 19 Methods to Monitor Chaperone‐Mediated Autophagy
- MAPK/JNK signalling: a potential Autophagy regulation pathway
- Mitochondrial Ca2+ signals in Autophagy
- Regulation and Function of Autophagy during Cell Survival and Cell Death
- Autophagy inhibitors
- Free Radicals in Cross Talk Between Autophagy and Apoptosis
- Autophagy Preceded Apoptosis in Oridonin-Treated Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells
- Autophagy in hypoxia-ischemia induced brain injury
- Autophagy in intracellular bacterial infection
- Autophagy in unicellular eukaryotes
- Evidence That Curcumin Suppresses the Growth of Malignant Gliomas in Vitro and in Vivo through Induction of Autophagy: Role of Akt and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signaling Pathways
- Autophagy and innate immunity: Triggering, targeting and tuning
- Autophagy is essential for effector CD8+ T cell survival and memory formation
- Molecular Mechanisms of Autophagy in the Cardiovascular System
- Cytotoxic Autophagy in Cancer Therapy
- TI-VAMP/VAMP7 and VAMP3/cellubrevin: two v-SNARE proteins involved in specific steps of the Autophagy/multivesicular body pathways
- New frontiers in promoting tumour cell death: targeting apoptosis, necroptosis and Autophagy
- The cell biology of Autophagy in metazoans: a developing story
- Understanding Autophagy in Cell Death Control
- The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) sustains Autophagy and limits apoptosis, promoting pancreatic tumor cell survival
- Erk1/2-dependent Phosphorylation of Gα-interacting Protein Stimulates Its GTPase Accelerating Activity and Autophagy in Human Colon Cancer Cells
- Autophagy in innate and adaptive immunity against intracellular pathogens
- Regulation of Liver Metabolism by Autophagy
- Author Correction: Autophagy maintains tumour growth through circulating arginine.
- Biological Functions of Autophagy Genes: A Disease Perspective
- RNA binding to p62 impacts selective Autophagy
- Intersections between Regulated Cell Death and Autophagy
- Ubiquitination of MAP1LC3B by pVHL is associated with Autophagy and cell death in renal cell carcinoma
- Autophagy without conjugation
- Chapter 16 – Autophagy and Autoimmunity
- Autophagy in the Heart